Introduction
Medical billing relies heavily on standardized codes that inform payers about the services, procedures, or supplies that were provided. While CPT and ICD-10 codes are well-known, HCPCS codes play a crucial role too, especially when it comes to durable medical equipment, medications, and certain outpatient services. For healthcare providers, grasping the significance of HCPCS codes is essential for ensuring accurate reimbursement and minimizing the risk of denials.
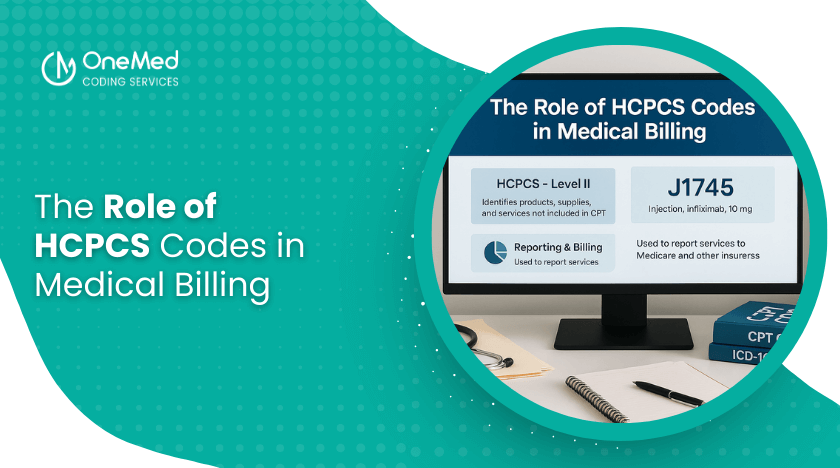
What Are HCPCS Codes?
HCPCS stands for Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System. These codes were created by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) to promote consistent reporting of medical services and supplies.
The system is split into two levels:
Level I (CPT Codes): These are numeric codes managed by the American Medical Association for procedures and physician services.
Level II (HCPCS Codes): These alphanumeric codes cover products, supplies, and services that aren’t included in CPT, such as durable medical equipment (DME), prosthetics, ambulance services, and medications.
Why HCPCS Codes Matter in Medical Billing
Unlike CPT codes, which are focused on medical procedures, HCPCS codes encompass the non-physician items and services that patients frequently require. Using these codes correctly ensures:
- Accurate Reimbursement: Payers depend on HCPCS codes to identify what equipment or service was provided.
- Compliance with Medicare & Medicaid Regulations: These codes are vital for billing government programs.
- Clarity in Claims: They help document supplies and services that support patient care but aren’t covered by CPT.
Without HCPCS codes, many services would go unbilled, leaving providers without compensation.
Let’s dive into some common examples of HCPCS codes and their significance:
- Durable Medical Equipment (DME): Think wheelchairs (E1038), oxygen equipment (E0424), and CPAP machines (E0601).
- Medications & Injections: This includes specific chemotherapy drugs, specialty medications, or injections that aren’t listed in the CPT.
- Supplies & Prosthetics: We’re talking about catheters, wound care supplies, prosthetic limbs, and orthotics.
- Ambulance Services: Both emergency and non-emergency transport fall under this category.
Each HCPCS code is quite specific, and using them correctly is crucial for ensuring that payers know exactly what services were provided.
The Connection Between HCPCS Codes and Compliance
HCPCS codes do more than just help with reimbursement—they also shield providers from compliance issues. If the wrong or outdated codes are used, it can lead to:
- Claim Denials: Payers will turn down claims if the HCPCS code doesn’t align with the service rendered.
- Audit Triggers: Frequent coding mistakes can raise suspicions of fraud or abuse.
- Delayed Payments: If modifiers are missing or descriptions are inaccurate, it can slow down the revenue cycle.
Using HCPCS codes accurately helps providers stay compliant with CMS guidelines and payer expectations.
Challenges Providers Encounter with HCPCS Codes
Even though they’re essential, managing HCPCS codes can be tricky because:
- They get updated every year, which means ongoing education is necessary.
- Some codes overlap with CPT, causing potential confusion.
- Documentation needs to be thorough to justify the billed supply or service.
- Payers might have specific requirements for certain codes.
Providers and billing teams need to stay vigilant to avoid costly errors.
Best Practices for Using HCPCS Codes
To minimize denials and boost reimbursement, providers should consider the following:
- Stay Updated: Make it a habit to check the annual CMS updates for any new, revised, or deleted HCPCS codes.
- Document Thoroughly: It's essential that clinical notes clearly support the use of any equipment or medication being billed.
- Use Modifiers Correctly: Modifiers such as NU (new equipment) or RR (rental) can significantly impact reimbursement rates.
- Train Staff Regularly: Regular training for coders and billers on payer-specific requirements for HCPCS codes is crucial.
- Leverage Technology: Utilizing coding software and claim scrubbing tools can help catch errors before submissions are made.
Conclusion
HCPCS codes play a vital role in medical billing, ensuring that providers receive payment for supplies, equipment, and services that fall outside of CPT coverage. When applied correctly, they facilitate accurate claims, compliance with payer regulations, and consistent revenue flow. By staying informed about updates, enhancing documentation practices, and training their teams, providers can fortify their billing processes and steer clear of unnecessary denials.


0 Comments